Abstract
In this paper, we explore the compression of deep neural networks by quantizing the weights and activations into multi-bit binary networks (MBNs). A distribution-aware multi-bit quantization (DMBQ) method that incorporates the distribution prior into the optimization of quantization is proposed. Instead of solving the optimization in each iteration, DMBQ search the optimal quantization scheme over the distribution space beforehand, and select the quantization scheme during training using a fast lookup table based strategy. Based upon DMBQ, we further propose loss-guided bit-width allocation (LBA) to adaptively quantize and even prune the neural network. The first-order Taylor expansion is applied to build a metric for evaluating the loss sensitivity of the quantization of each channel, and automatically adjust the bit-width of weights and activations channel-wisely. We extend our method to image classification tasks and experimental results show that our method not only outperforms state-of-the-art quantized networks in terms of accuracy but also is more efficient in terms of training time compared with state-of-the-art MBNs, even for the extremely low bit width (below 1-bit) quantization cases..
Method
We explore the distribution of weights and dedicate to find the optimal quantization scheme of MBQ under the distribution assumption. By minimizing the expected mean square error, a lookup table based strategy is proposed to optimize the quantization schemes with very few computational cost during the iterations. In addition, We model the quantization effect upon the loss of network with Taylor expansion and formulate a metric to evaluate the quantization sensitivity of weights, i.e., the loss variation of the network with the quantization of weights. Since only gradients of quantized weights are required, which could be directly obtained from the backward propagation, the metric can be easily computed, and thus we can adaptively adjust the quantization bit-width of weights and activations in the training process without too much computational load.
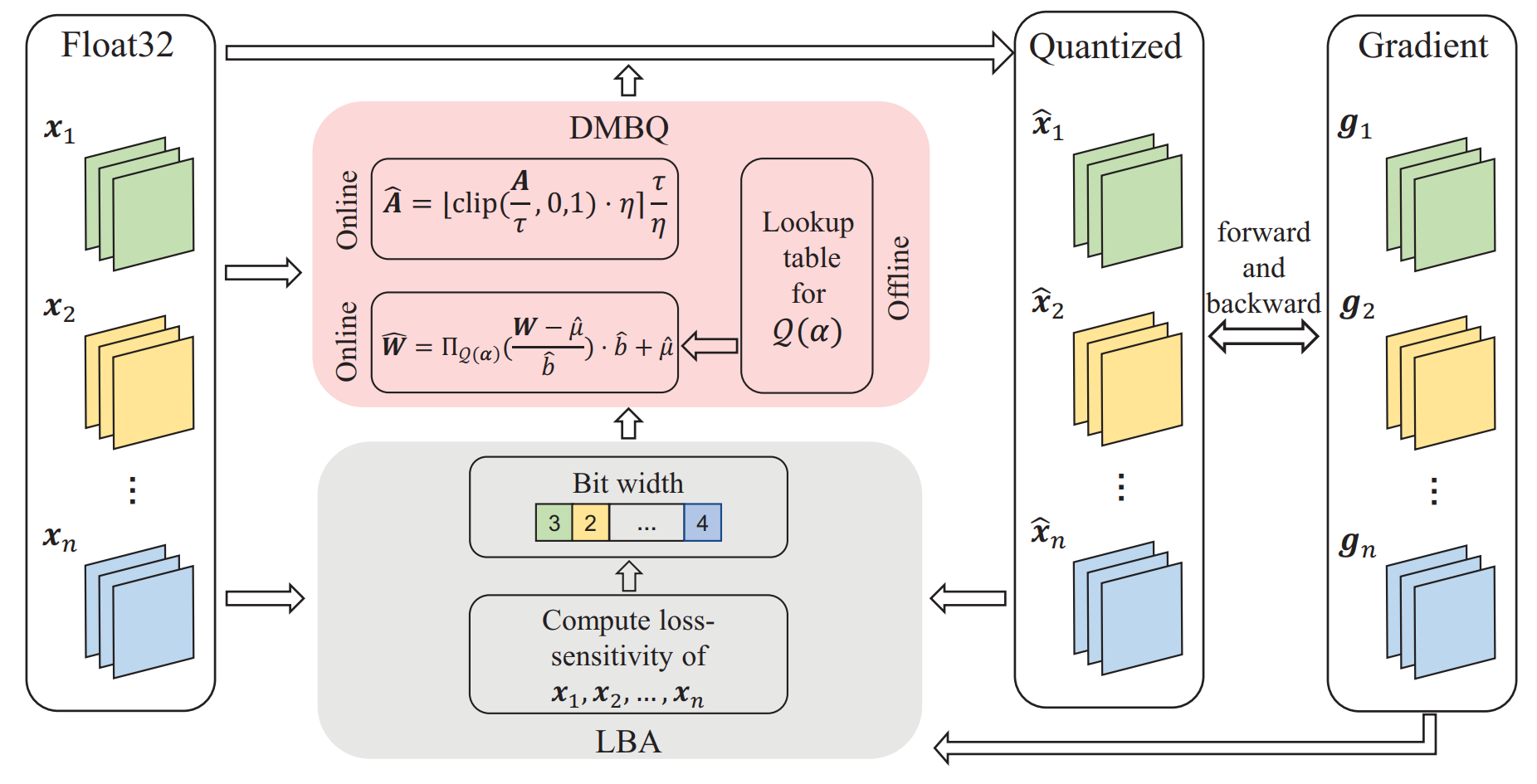
Figure 1. An overview of our proposed quantization method.
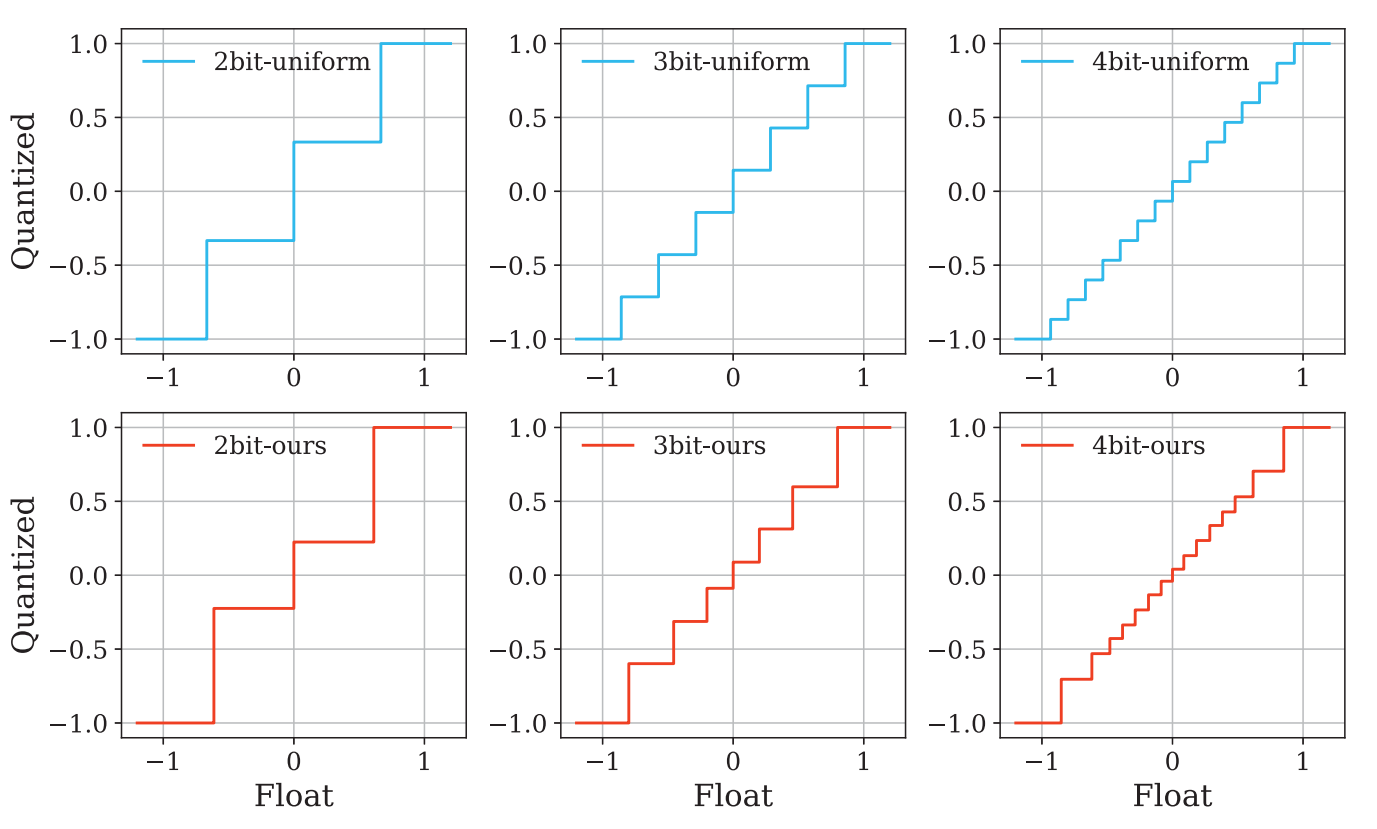
Figure 2. Comparison between our DMBQ and uniform quantization.
Experiments
Table 1. Comparison of different quantization methods on ILSVRC12.
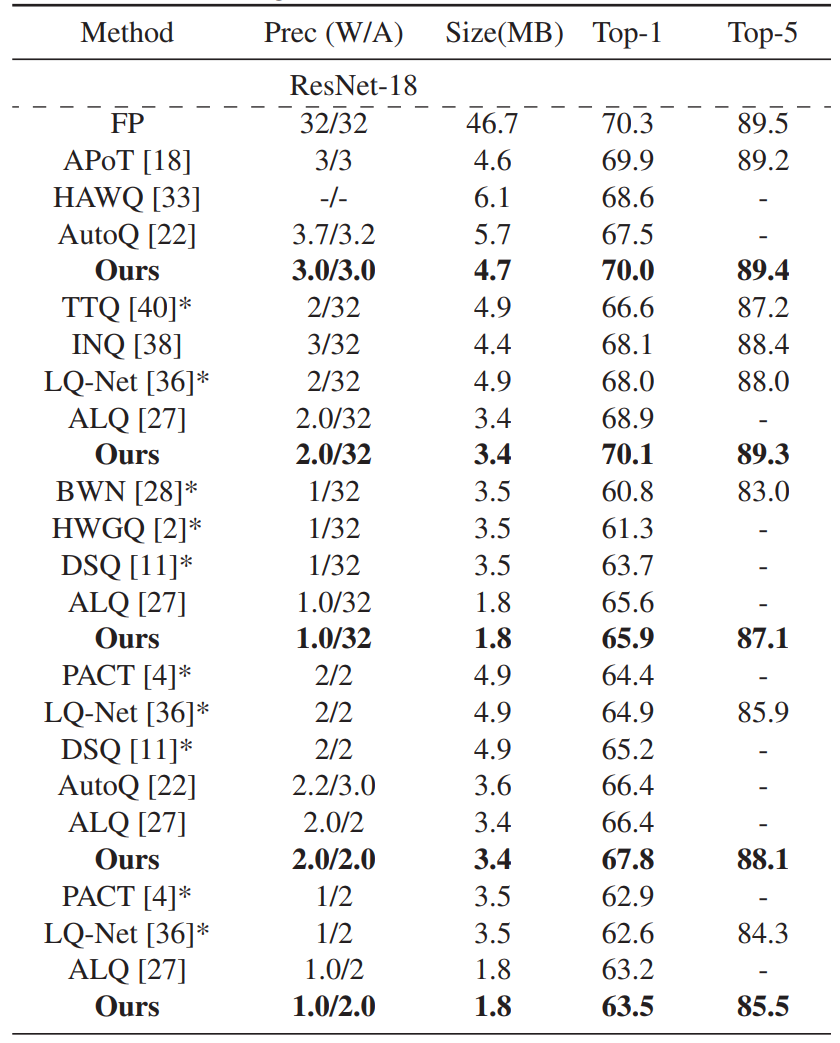
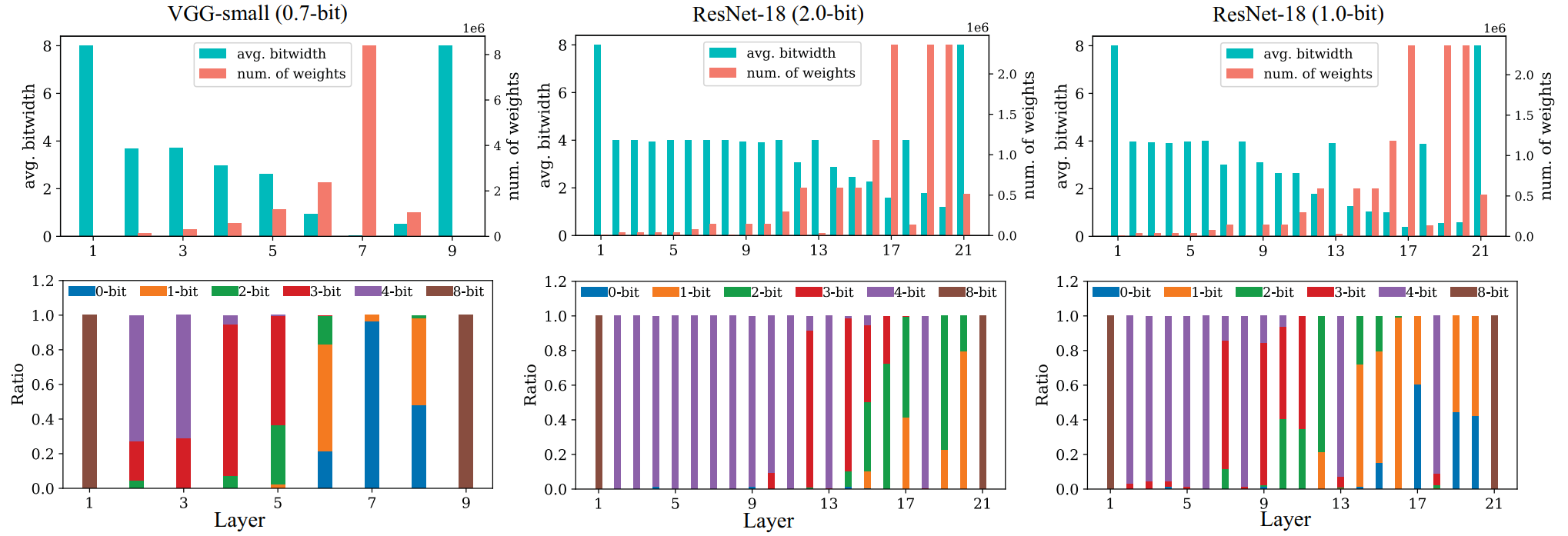
Figure 3. The statistical characteristics of channel-wise quantization models.
More Details
- File
- Presentation
- Available source code: GitHub
Bibtex
@InProceedings{zhao2021distribution,
author = {Sijie Zhao and Tao Yue and Xuemei Hu},
title = {Distribution-aware Adaptive Multi-bit Quantization},
booktitle = {The IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR)},
month = {June},
year = {2021}
}